Amsterdam, operational phase of the restoration of Rembrandt's Night Watch begins
After five years of preparation, today a team of eight restorers from the Rijksmuseum in Amsterdam officially began the restoration of the Night Watch, Rembrandt’s masterpiece. This start marks the beginning of the second phase, or the operational phase, of the largest research and restoration project ever devoted to this Rembrandt masterpiece (the first phase was surveys). The removal of the old varnish will allow the painting to be preserved for future generations. Visitors can follow the process live in the Night Watch Gallery, where the restoration work is being carried out with microscopic precision in the transparent glass chamber.
“The beginning of the restoration phase is full of anticipation,” emphasizes Taco Dibbits, director of the Rijksmuseum. "The removal of the varnish will reveal the eventful history of the Night Watch , and it will be a truly unique experience for the visiting public to be able to follow the process from so close up."
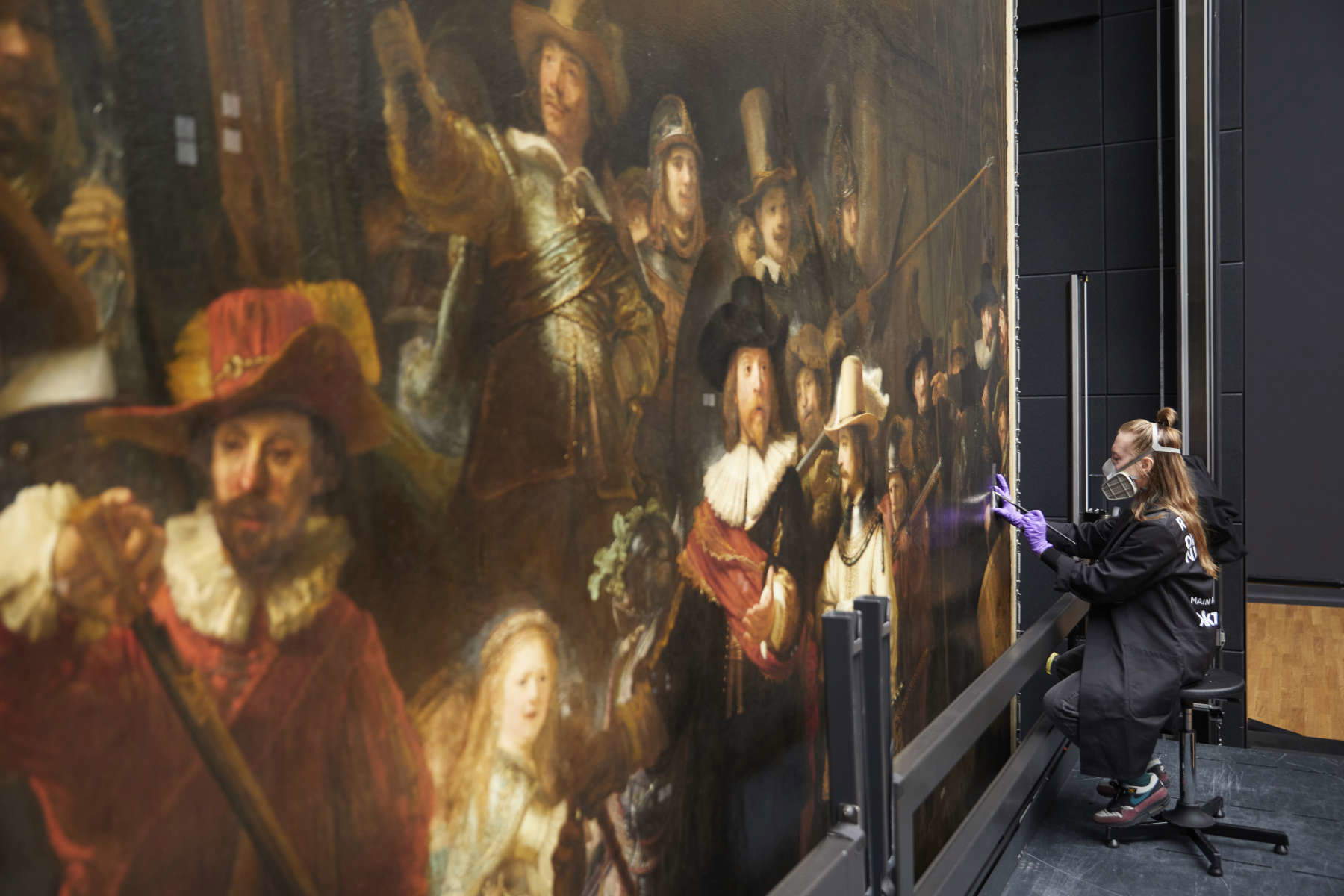
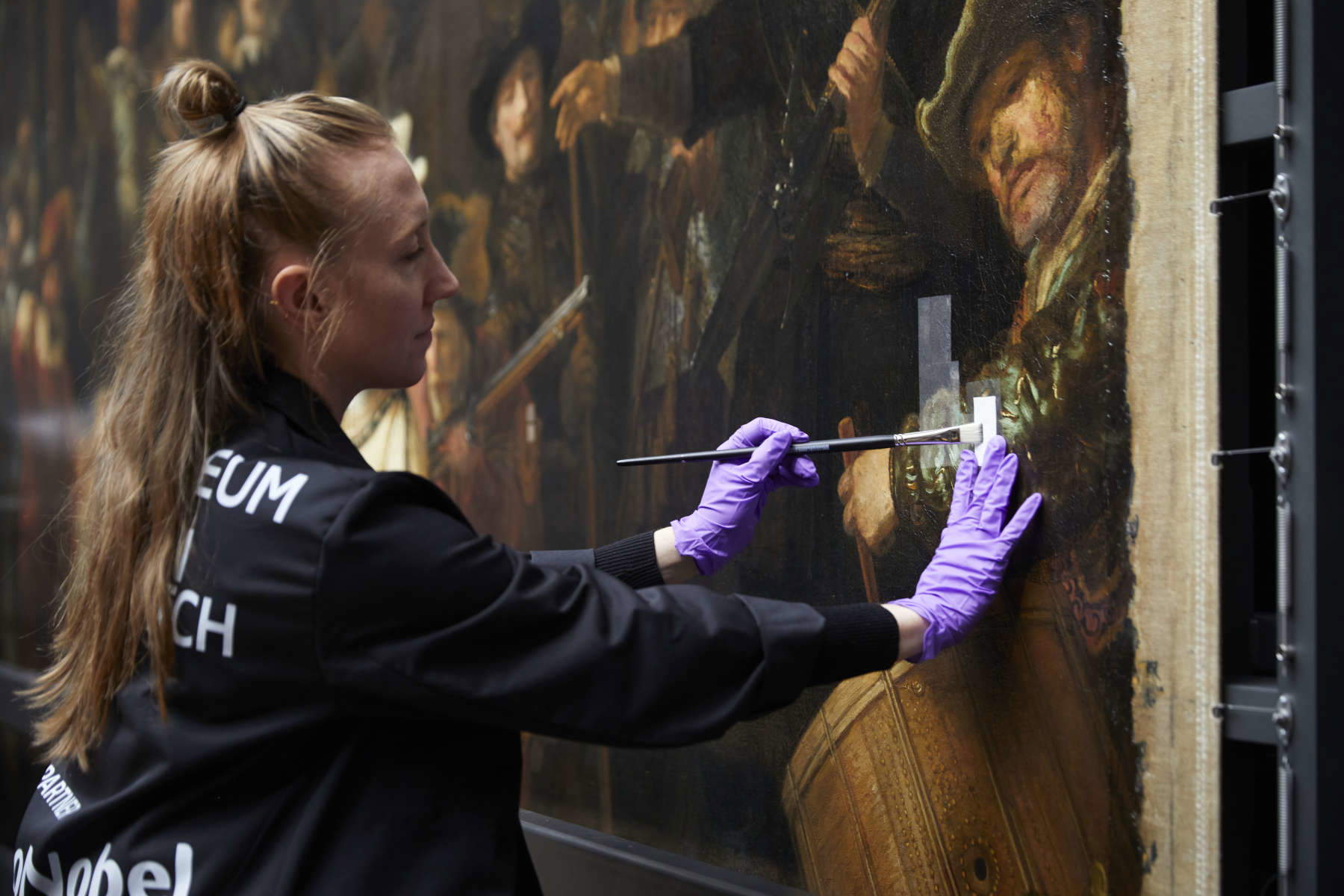
Restorers at the Rijksmuseum are using a special type of fabric to remove the layers of varnish applied to the painting following restoration in 1975-1976. Restorers place the fabric, prepared with a solvent, against the surface of the Ronda at night for a short, limited amount of time. The paint is solubilized and absorbed into the fabric. Then, using a microscope, they carefully remove any remnants of even older paint with cotton swabs. This moment is, according to the museum, the culmination of years of scientific research, applying this technique to other paintings, and conducting tests on the stressa Ronda at night.
Over the past five years, a large team of conservators, curators, scientists and other specialists has been studying the Ronda at night using the most advanced technologies: from digital imaging to scientific and technical studies, from computer science to artificial intelligence. This work has led to various breakthroughs in our understanding of the painting’s condition and the artist’s way of working.
The team collaborates with experts from the Rijksmuseum’s main partner for this project, AkzoNobel, as well as the Netherlands Cultural Heritage Agency (RCE), Delft University of Technology (TU Delft), theUniversity of Amsterdam (UvA), Amsterdam University Medical Centre (AUMC), University of Antwerp (UA), Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam (VU), Eindhoven University of Technology (TU/e), and the National Gallery of Art in Washington DC.





 |
| Amsterdam, operational phase of the restoration of Rembrandt's Night Watch begins |
Warning: the translation into English of the original Italian article was created using automatic tools. We undertake to review all articles, but we do not guarantee the total absence of inaccuracies in the translation due to the program. You can find the original by clicking on the ITA button. If you find any mistake,please contact us.